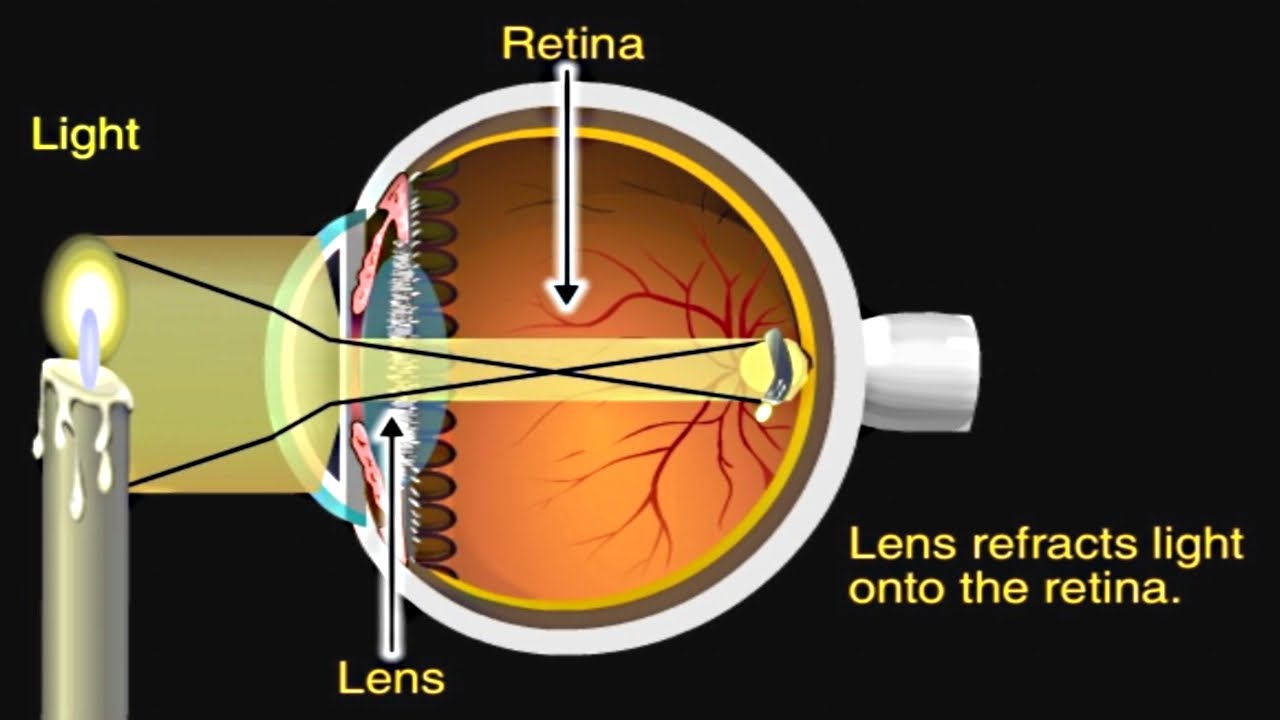
 The eye is the organ of sight and is shaped as a slightly irregular hollow sphere. Various structures in the eye enable it to translate light into recognizable images. Among these are the cornea, the lens, and the retina.
The eye is the organ of sight and is shaped as a slightly irregular hollow sphere. Various structures in the eye enable it to translate light into recognizable images. Among these are the cornea, the lens, and the retina. Light first passes through the cornea, a clear dome-like structure covering the iris, or colored part, of the eye. The cornea bends, or refracts, the light onto the lens. The light is then refracted a second time while passing through the lens, finally focusing on the retina. The retina is the light sensitive part of the eye. Impulses travel down the optic nerve to the occipital lobe of the brain, which then interprets the image in the correct perspective.
The shape of the eye is very important in keeping the things we see in focus. If the shape of the eye changes, it affects a person’s vision.
Normally, light is precisely focused onto the retina at a location called the focal point. A nearsighted eye is longer from front to back than a normal eye causing light to be focused in front of the retina instead of directly onto it. This makes it difficult to see objects that are far away. Glasses with concave lenses are used to correct nearsightedness. The concave lens focuses light back onto the focal point of the retina.
Farsightedness occurs when the length of the eye is too short. Light is focused at a point behind the retina, making it difficult to see objects that are up close. A convex lens is used to correct farsightedness because it directs the focal point back onto the retina.
How Your Eyes Work
When light rays reflect off an object and enter the eyes through the cornea (the transparent outer covering of the eye), you can then see that object. Rods and Cones in the retina
The cornea bends, or refracts, the rays that pass through the round hole of the pupil. The iris (the colored portion of the eye that surrounds the pupil) opens and closes, making the pupil bigger or smaller. This regulates the amount of light passing through.
The light rays then pass through the lens, which changes shape so it can further bend the rays and focus them on the retina. The retina, which sits at the back of the eye, is a thin layer of tissue that contains millions of tiny light-sensing nerve cells. These nerve cells are called rods and cones because of their distinct shapes.
Cones are concentrated in the center of the retina, in an area called the macula. When there is bright light, cones provide clear, sharp central vision and detect colors and fine details.
Rods are located outside the macula and extend all the way to the outer edge of the retina. They provide peripheral or side vision. Rods also allow the eyes to detect motion and help us see in dim light and at night.
These cells in the retina convert the light into electrical impulses. The optic nerve sends these impulses to the brain, which produces an image.
The human eye is an organ that reacts to light and has several purposes. As a sense organ, the mammalian eye allows vision. Rod and cone cells in the retina allow conscious light perception and vision including color differentiation and the perception of depth. The human eye can distinguish about 10 million colors and is possibly capable of detecting a single photon.
Similar to the eyes of other mammals, the human eye's non-image-forming photosensitive ganglion cells in the retina receive light signals which affect adjustment of the size of the pupil, regulation and suppression of the hormone melatonin and entrainment of the body clock.
Visual perception is the ability to interpret the surrounding environment by processing information that is contained in visible light. The resulting perception is also known as eyesight, sight, or vision (adjectival form: visual, optical, or ocular). The various physiological components involved in vision are referred to collectively as the visual system, and are the focus of much research in Linguistics, psychology, cognitive science, neuroscience, and molecular biology, collectively referred to as vision science.
Light entering the eye is refracted as it passes through the cornea. It then passes through the pupil (controlled by the iris) and is further refracted by the lens. The cornea and lens act together as a compound lens to project an inverted image onto the retina.
The retina consists of a large number of photoreceptor cells which contain particular protein molecules called opsins. In humans, two types of opsins are involved in conscious vision: rod opsins and cone opsins. (A third type, melanopsin in some of the retinal ganglion cells (RGC), part of the body clock mechanism, is probably not involved in conscious vision, as these RGC do not project to the lateral geniculate nucleus but to the pretectal olivary nucleus.) An opsin absorbs a photon (a particle of light) and transmits a signal to the cell through a signal transduction pathway, resulting in hyper-polarization of the photoreceptor. Rods and cones differ in function.


0 Comments